Data Warehouse
Data warehouse is an architecture for organizing information system. It
is a process for building decision support systems and knowledge
management enviroment that supports both day-to-day tactical decision
making and long-term business strategies. Bill Inmon
"Subject-oriented, integrated, time variant,
non-volatile collection of data in support of management's decision
making process."
Data Mart
A data mart is a collection of subject areas organized for decision
support system based on the needs of a given department.
Typically, the database design for a data mart is built as star
schema structure that is optimal for the needs of the users found in
the department. There are two kinds of data marts - dependent and
independent. A dependent data mart is one whose source is a data
warehouse. An independent data mart is one whose source is
legacy applications or OLTP environment.
Operational Data Store(ODS)
An operational data store is an integrated, subject-oriented,
volatile(including update/deletion), current valued structure designed
to serve operational users as they do high performance integrated
processing.
OLTP(Online Transaction Processing)>
OLTP is a class of program that facilitates and manages transaction-oriented applications,
typically for data entry and retrieval transaction processing. OLTP systems are optimized for data entry operations.
e.g. Order Entry, Banking, CRM, ERP applications etc.
Data Warehouse vs Operational
| Data
Warehouse |
Operational/Transactional |
| Subject oriented |
Application oriented |
| Summarized, refined &
detailed |
Detailed |
| Represents value over time |
Accurate as of moment |
| Supports managerial needs |
Supports day-to-day needs |
| Read only data |
Can be updated |
| Batch processing |
Real time transactions |
| Completely different life cycle |
Software Development Life Cycle |
| Analysis driven |
Transaction driven |
| Dimensional model |
Entity Relational Diagram |
| Large amount of data |
Small amount of data |
| Relaxed availability |
High availability |
| Flexible structure |
Static structure |
DW Methodologies
| Top-Down | Bottom-Up | Hybrid | Federated | |
| Practitioner |
Bill Inmon | Ralph Kimball | Many practitioners | Doug Hackney |
| Emphasize | Data Warehouse | Data Marts |
DW and data marts |
Integrate heterogeneous BI
environments |
| Design |
Enterprise based normalized
model; marts use a subject orient dimensional model |
Dimensional model of data mart,
consists star schema |
Start enterprise and local
models; one or more star schemas |
An achitecture of architectures;
share dimensions, facts, rules, definitions across organizations |
| Architect |
Multi-tier comprised of staging
area and dependent data marts |
Staging area and data marts |
High-level normalized enterprise
model; initial marts |
Reality of change in
organizations and systems |
| Data set |
DW atomic level data; marts
summary data |
Contains both atomic and summary
data |
Populates marts with atomic and
summary data via a non-persistent staging area. |
Use of whatever means possible
to integrate business needs |
Agile Developement
Agile methodology emphasize close collaboration between the technical team and business experts;
face-to-face communication; self-organizing teams; frequent delivery of business value releases.
3D Lifecycle
Dimensional Data Warehouse Development Lifecycle -
Our approach Agile data warehouse development with integrating iterative and data driven components.
Enterprise data warehouse data model is suggested as dimensional with conformed subject areas.
The goal of 3D methodology is to define strategies that enable data warehouse practitioners to work
effectively on development and deliverables. This does not mean "one size fits all" methodology.
Instead, consider 3D life cycle as a collection of philosophies that will enable
technical and business experts to work together effectively to maximize ROI.
3DLC is an adaptable process framework, intended to be tailored by project teams
that will select the elements of the process that are appropriate for their needs.
Business Intelligence (BI)
Business Intelligence is a set of business processes for collecting
and analying business information. BI functions include trend
analysis, aggregation of data, drilling down to complex levels of
detail, slice-dice, data rotation for comparative viewing.
E. F. Codd(father of the relational database)'s 12 rules for OLAP
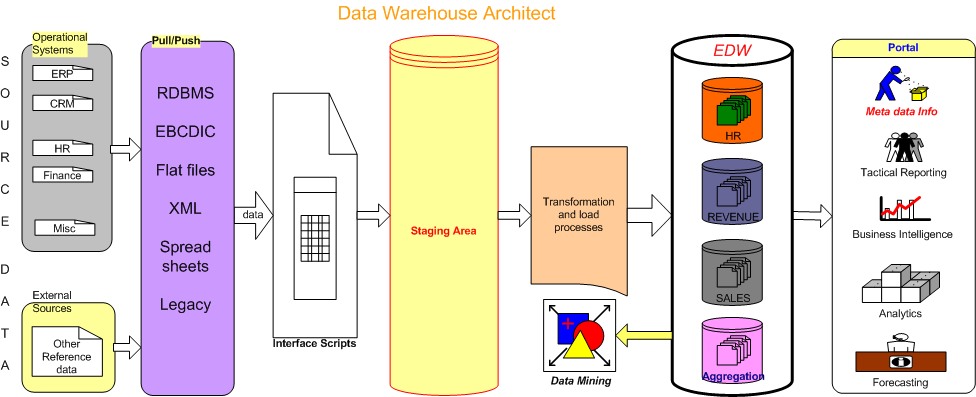
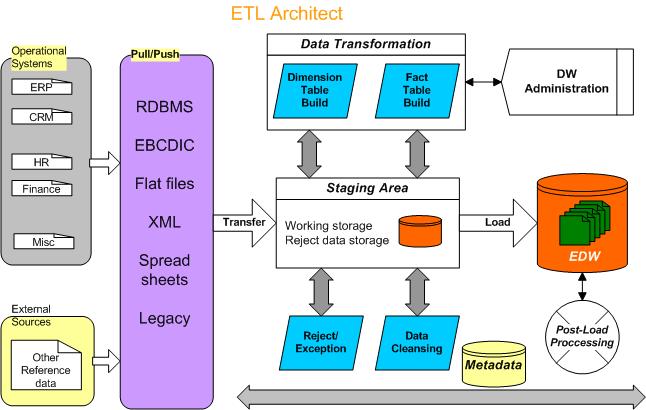
Extract clean Transform Load(ETL)
Data loading is a major process in data warehouse. It
comprises 50% to 75% of any data warehousing effort. Effective
ETL process represent main success of data warehouse project.
Data Mining
Generally speaking data mining is knowledge discovery process of analyzing data from
different perspectives and categorize it into useful information. Technically, data mining
is the process of finding correlations or patterns across fields in large databases.
Meta Data Management
Data about data. Metadata describes the information
stored in the data warehouse. It can be defined into three
categories:-
|
Copyright © 2007 DW Mantra Inc. All rights reserved. |